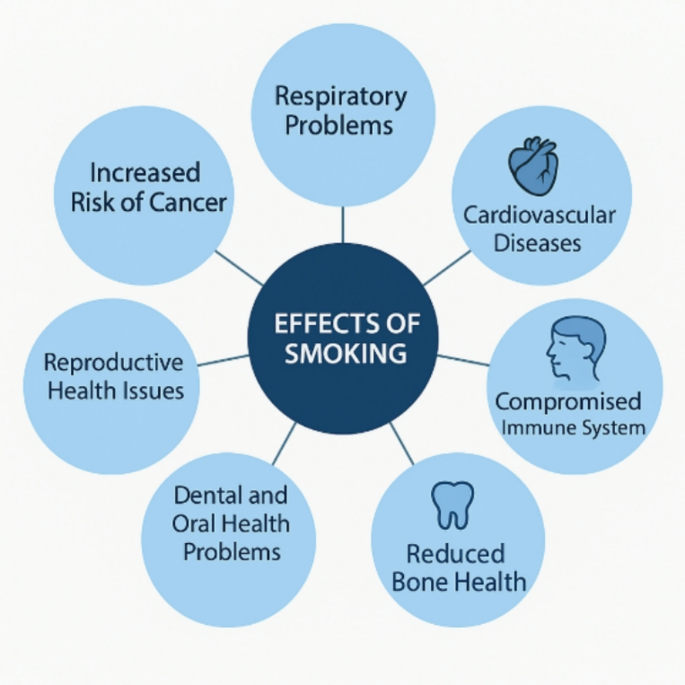
The Multifaceted Impact of Smoking: An Informative Exploration
Smoking remains one of the most contentious topics in public health, given its profound implications for individual and societal health outcomes. This article dives into various dimensions of smoking—from its effects on the respiratory system to its connection with chronic diseases—supported by recent and relevant research.
Effects of Smoking on the Respiratory System
Recent research by Vásconez-González et al. (2023) sheds light on the devastating effects of smoking marijuana on the respiratory system. Their systematic review elucidates that substances inhaled during smoking can lead to bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other long-term respiratory issues. The findings emphasize not only the immediate discomfort experienced by users but also a potentially ongoing deterioration of lung health over time.
Understanding Chronic Inflammation and Immune Function
Elisia et al. (2020) examine how smoking influences chronic inflammation and immune function. Their study highlights that smoking can lead to changes in blood cell composition, thereby weakening the immune response. This compromised immunity places smokers at a higher risk of infections and chronic diseases. The research calls attention to the urgent need for public health interventions to mitigate smoking’s consequences on overall health.
Smoking and Cardiovascular Health
In the cardiovascular realm, studies illustrate how smoking acts as a significant risk factor for heart disease. Giulietti et al. (2020) performed a comprehensive review on pharmacological strategies for smoking cessation, underlining the critical connection between smoking and cardiovascular health. Their research indicates that even reducing cigarette intake can lead to substantial health benefits, reinforcing the narrative that any cessation is beneficial.
Infectious Diseases and Smoking
The nexus between smoking and infectious diseases is explored by Jiang et al. (2020). The narrative review discusses how the act of smoking weakens the immune response, making smokers more susceptible to illnesses. Whether through respiratory infections or prolonged recovery times, the statistics highlight that smoking directly correlates with higher rates of infectious disease, necessitating targeted health messaging.
Societal Perceptions and Behaviors
Understanding smoker characteristics can also inform public health strategies. Kamruzzaman et al. (2021) investigated smokers’ perceptions of their health and social environments in Bangladesh. Their study reveals that societal norms strongly influence smoking behavior, suggesting that altering these perceptions could pave the way for more effective public health campaigns.
The Role of Age and Gender
In the context of age and gender, Chang et al. (2021) conducted a meta-analysis focusing on how these factors affect health risks associated with smoking. Their findings indicate significant differences in the health impact of smoking based on demographic variables, underscoring the need for tailored interventions that consider these factors.
Historical Context of Smoking and Health
The long-standing relationship between smoking and health was notably reviewed by Breslow (1980), who provides an early understanding of the implications of smoking. His work set the groundwork for advances in public health recommendations and tobacco cessation programs that followed.
Current Research on Smoking Cessation Technologies
As technology evolves, so do interventions aimed at helping smokers quit. A recent study examined pharmacological approaches to smoking cessation, emphasizing new medications and behavioral therapies designed to support individuals in their quitting journeys. Technologies such as mobile apps and telehealth are playing an increasingly vital role in providing resources and support.
Smoking and Mental Health
Recent discussions have also sparked interest in the psychological dimensions of smoking. Emerging studies suggest that smoking is not merely a physical habit but is deeply intertwined with mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. The relationship appears to be bidirectional; while smoking may exacerbate mental health issues, those suffering from such issues often turn to smoking for relief.
Community and Policy Interventions
Community-based interventions have shown promise in combating smoking rates. Collaborative efforts between health organizations and community leaders seek to foster environments that promote healthier behaviors. Policy changes, such as increased taxation and restriction of marketing of tobacco products, have also been effective in reducing smoking prevalence.
Ethical Considerations
As with many public health initiatives, ethical considerations arise when dealing with smoking cessation programs. Addressing the disparities faced by marginalized communities, ensuring access to cessation resources, and combating stigmatization are vital components of effective public health strategies.
Future Directions
As research continues, an interdisciplinary approach combining insights from medicine, psychology, policy, and community health is essential. Understanding the complexity of smoking behavior allows for more robust public health strategies and tailored interventions that address the multifaceted nature of this issue.
In summary, smoking remains a critical public health challenge, characterized by its extensive impact across various health domains and demographics. Ongoing research is crucial for understanding its complexities and for developing effective health interventions aimed at reducing smoking prevalence and its associated health risks.