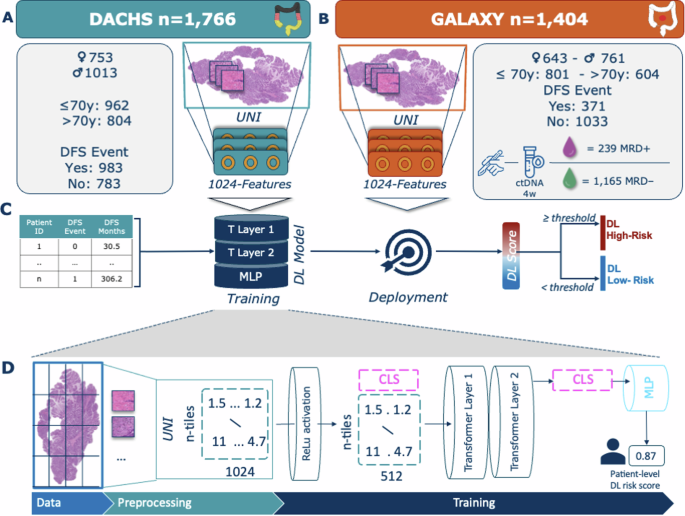
Recent Advances in Colorectal Cancer Research and Management
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. This article examines the latest advancements in understanding CRC, focusing on incidence rates, predictive biomarkers, treatment options, and the implications of technological innovations like artificial intelligence.
Cancer Statistics
According to Siegel et al. (2024), the overall incidence of colorectal cancer continues to rise, with specific demographic groups seeing the most significant increases. The detailed analysis emphasizes the importance of early detection and regular screening, especially in high-risk populations.
Risk Factors and Disease Recurrence
A population-based study by Boute et al. explores the cumulative incidence and risk factors associated with recurrence after curative resection of stage II-III colorectal cancer. Their findings highlight critical survival rates and underline the necessity of tailored surveillance strategies post-surgery for improved patient outcomes.
Another cohort study from Denmark, as reported by Nors et al., provides insights into the timing of disease recurrence in stages I to III, reinforcing the notion that continuous monitoring is key to managing long-term recovery.
Treatment Approaches
Surgical Options
One notable study by Kanemitsu et al. challenges traditional treatment paradigms by comparing hepatectomy followed by chemotherapy versus surgery alone for liver-only metastatic colorectal cancer. This research, a phase II/III randomized trial, sheds light on the effectiveness of integrated treatment strategies.
Targeted Monitoring Techniques
Recent investigations have explored the role of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in monitoring recurrence. Oki et al. outlined how ctDNA can serve as a prognostic tool in metastatic colorectal cancer, providing valuable insights into disease progression and treatment efficacy.
Biomarkers in Cancer Treatment
García-Alfonso et al. discuss updates on biomarkers essential for CRC diagnosis and treatment. These biomarkers can guide therapeutic decisions, helping identify which patients may benefit from adjuvant therapy and those at a higher risk of recurrence.
Artificial Intelligence in Colorectal Cancer
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into pathology is rapidly evolving. A study spearheaded by Shmatko et al. underscores how AI methods can enhance cancer research, particularly in histopathological assessments, potentially leading to more personalized treatment approaches.
AI’s Role in Predictive Analytics
A study by Jiang et al. demonstrates end-to-end prognostication in colorectal cancer using deep learning techniques. This approach enables more precise risk stratification and personalized treatment planning, transforming how healthcare providers approach patient management.
The Importance of Immune Response
Research by Galon et al. emphasizes the complexity of immune cell interactions within tumors and how these dynamics can predict clinical outcomes. Understanding the relationship between immune response and tumor behavior can better inform treatment strategies.
Challenges in Screening and Follow-Up
Diagnostic accuracy in follow-up tests for detecting recurrences is critically analyzed in research published by Liemburg et al. Their systematic review and meta-analysis highlight gaps and challenges in current methodologies, suggesting the need for improved approaches that enhance detection rates.
Practical Considerations in Adjuvant Therapy
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines, as updated by Baxter et al. (2022), guide decisions regarding adjuvant therapy for stage II colon cancer. These updates reflect ongoing research to refine treatment frameworks to optimize patient outcomes.
Prognostic Challenges and Opportunities
The role of tumor-stroma interactions in patient prognosis is explored by Huijbers et al. The study indicates that the proportion of tumor stroma can serve as a significant prognostic indicator, offering new avenues for risk assessment in colorectal cancer.
Emerging Technologies in Clinical Practice
Publications from Kiehl et al. and Zhou et al. emphasize the potential of deep learning in predicting lymph node status and overall patient stratification for colon adenocarcinoma. These technological advances could redefine how clinicians approach diagnosis and treatment in clinical settings.
Conclusion
As research in colorectal cancer unfolds, the importance of multidisciplinary approaches and incorporating cutting-edge technologies becomes increasingly clear. Enhanced diagnostic capabilities, innovative treatment strategies, and a focus on personalized medicine promise to improve outcomes for patients battling this formidable disease.