“Revolutionizing Brain Tumor Classification with Deep Learning”
Revolutionizing Brain Tumor Classification with Deep Learning
Understanding Deep Learning in Medical Imaging
Deep learning refers to a subset of artificial intelligence that uses artificial neural networks to analyze complex data patterns. In medical imaging, this technology is crucial for accurately diagnosing conditions such as brain tumors. Traditional classification methods often rely on manual interpretation, which can be subjective and error-prone. In contrast, deep learning automates this process, enhancing diagnostic precision through its ability to learn from vast amounts of labeled data.
For example, a convolutional neural network (CNN) can learn from thousands of MRI scans to identify subtle patterns that may indicate the presence of a tumor. This capability not only speeds up diagnosis but also minimizes human error, making it a game-changer in medical practice.
Key Components of Deep Learning for Tumor Classification
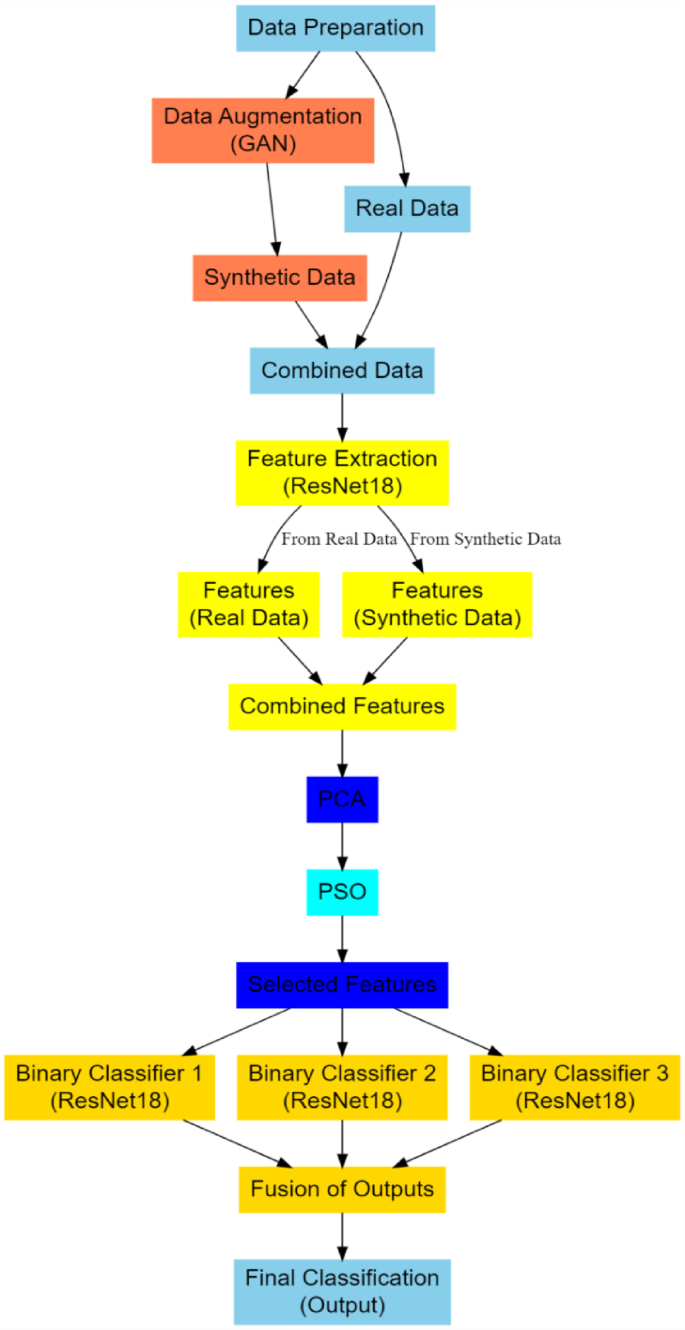
At the heart of deep learning applications in brain tumor classification are several key components: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for data augmentation, ResNet models for feature extraction, and Deep Multiple Fusion Networks (DMFN) for classification.
GANs consist of two neural networks— a generator and a discriminator—that compete against each other. The generator aims to produce synthetic images that mimic real ones, while the discriminator assesses the authenticity of images. This setup helps overcome challenges related to limited labeled data, which is often a bottleneck in medical imaging tasks, enabling more robust models to be trained.
Meanwhile, ResNet models, like ResNet18, utilize skip connections to alleviate the vanishing gradient problem, which can occur in deeper networks. This property makes ResNet architectures particularly effective for medical image analysis, as they can capture intricate patterns while maintaining computational efficiency.
Lifecycle of Brain Tumor Classification with Deep Learning
The classification process typically follows these steps:
-
Data Collection and Preprocessing: Relevant medical images are gathered—often from datasets such as BraTS—then preprocessed through normalization and skull stripping to ensure uniformity.
-
Data Augmentation: Using GANs, additional synthetic training data is generated to counteract class imbalances found in medical datasets, which can help improve the model’s overall robustness.
-
Feature Extraction: Once training data is prepared, ResNet18 is employed to extract high-level features from the images, effectively summarizing essential characteristics while retaining critical information.
-
Feature Selection: Techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) combined with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) are utilized to optimize feature selection, enhancing classifier accuracy by focusing on the most relevant features.
- Classification: Finally, the DMFN architecture performs classification by aggregating results from multiple ResNet models, each specializing in differentiating pairs of tumor classes.
Practical Example: DMFN for Tumor Classification
The DMFN framework operates effectively in distinguishing various brain tumor types, including gliomas and meningiomas. For instance, it employs three separate ResNet18 models, each tasked with binary classification between two tumor categories. This modular approach not only enhances prediction accuracy but also reduces confusion between overlapping feature spaces.
By training each model individually and fusing results via a weighted mechanism—where the contribution of each model is informed by its performance on validation data—the DMFN can leverage the strengths of different classifiers. The final classification output is the class with the highest aggregate probability, effectively streamlining decision-making.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
A frequent challenge in deep learning for medical applications is overfitting, particularly when training on small datasets. To mitigate this, several strategies can be implemented:
-
Use of Data Augmentation: Employing GANs helps generate diverse synthetic training examples, reducing the likelihood of overfitting on limited real data.
- Implementing Regularization Techniques: Techniques such as dropout can be incorporated during training to prevent reliance on specific subsets of neurons, ensuring that the model generalizes better to unseen data.
By recognizing and addressing these pitfalls, practitioners can develop more robust models that maintain high accuracy across varying clinical scenarios.
Tools and Metrics in Practice
Tools commonly used in this space include TensorFlow and PyTorch for model implementation, along with Keras for high-level neural network building. Metrics such as accuracy, F1 score, and Area Under the Curve (AUC) evaluate model performance, ensuring that the deep learning models are not just fitting the training data but generalizing well to new cases.
Variations and Alternatives in Classification Approaches
While the proposed framework focuses on GANs, ResNet, and DMFN, variations exist that utilize alternative architectures like EfficientNet or DenseNet. These options often yield different trade-offs in terms of computational efficiency and performance. For organizations with limited computational resources, simpler models may suffice, whereas larger institutions may benefit from the enhanced capabilities of more complex architectures.
Deciding which approach to implement depends on the specific context and goals, including factors like data availability, compute power, and the necessity for real-time diagnosis.
FAQ
What are the primary benefits of using deep learning in medical imaging?
Deep learning enhances diagnostic accuracy by automating image analysis, reducing subjectivity, and enabling faster evaluations. Furthermore, it leverages vast datasets to identify complex patterns that may not be visible to the human eye.
How does GAN-based data augmentation improve model performance?
GANs generate realistic synthetic images that enrich training datasets, addressing issues like class imbalance and limited sample sizes. This leads to models that are better prepared to handle a variety of real-world scenarios.
Can I use other architectures besides ResNet for feature extraction?
Yes, while ResNet is popular for its performance and efficiency, architectures like EfficientNet or DenseNet can also be used. The choice often depends on the specific requirements of the task, such as the need for speed versus accuracy.
Why is feature selection important in deep learning models?
Effective feature selection reduces dimensionality, which simplifies the model and can improve overall performance. It also helps retain the important variances that distinguish different classes, thus enhancing classification accuracy.