Understanding Corneal Opacity: A Global Health Challenge
What is Corneal Opacity?
Corneal opacity refers to the loss of transparency in the corneal tissue, a vital component of the eye essential for proper vision. The cornea serves as the eye’s primary refractive medium; its clarity is crucial for focusing light accurately onto the retina. When the cornea becomes opaque, whether due to scarring, structural alterations, or disease, it can lead to significant vision impairment. This condition emerges from various causes, including ophthalmic trauma, infections, hereditary disorders, surgical interventions, and other pathological changes.
Global Impact of Corneal Opacity
Corneal opacity is a major contributor to visual impairment worldwide, accounting for an estimated 5.1% of all blindness cases. The burden is especially pronounced in low- and middle-income countries, where healthcare resources may be limited. In these areas, individuals suffering from corneal opacities face significant health risks, underlining the importance of addressing this condition not just as a medical issue but as a social and economic challenge.
Clinical Evaluation and Challenges
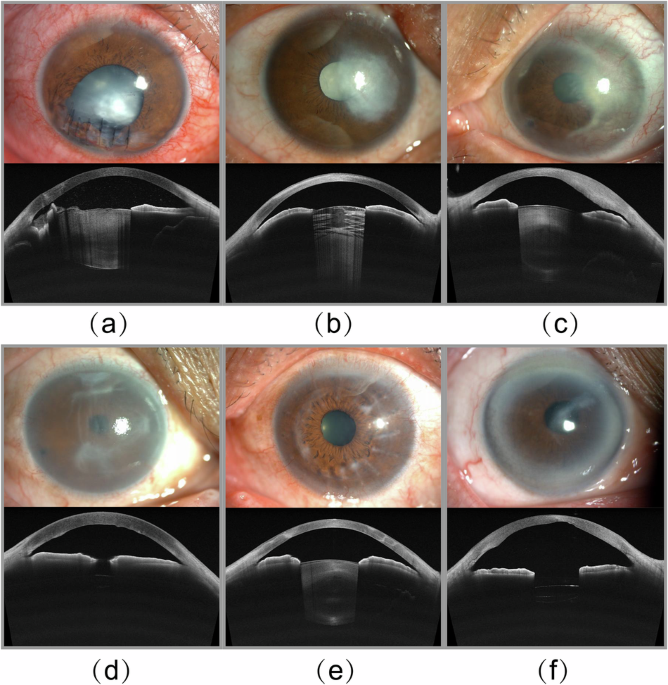
Currently, the clinical evaluation of corneal opacity is fraught with difficulties. Many ophthalmologists, particularly in under-resourced regions, rely on subjective assessments via slit-lamp examinations to gauge corneal status. While tertiary care centers may have advanced diagnostic tools like anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT), the interpretation of these images can be complex. This diagnostic variability can lead to inconsistent treatment decisions due to the subjective nature of corneal assessments.
For instance, mild or superficial opacities could respond well to antifibrotic agents aimed at enhancing corneal clarity. Conversely, more advanced cases might require procedures like phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK), a precise laser ablation technique to remove diseased tissue. In severe cases where vision loss is significant, corneal transplantation—either penetrating keratoplasty (PK) or deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK)—is often necessary. The inconsistency in grading corneal opacities, however, complicates the determination of the most appropriate treatment protocols.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Encouragingly, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning technologies offer promise in improving the assessment of corneal opacities. By utilizing multimodal inputs from AS-OCT and anterior segment photographs (ASP), deep learning algorithms can extract detailed features, allowing for more precise classification and quantification of corneal opacities.
This integrative approach enhances diagnostic consistency, making it easier for clinicians to make informed decisions tailored to individual patients. Moreover, as AI models evolve, they could even synthesize AS-OCT-like images from basic ASP inputs, broadening diagnostic capabilities in regions where access to advanced imaging tools is limited.
Nonetheless, the success of these AI applications hinges on the availability of high-quality datasets. Current research predominantly focuses on specific conditions associated with corneal opacities but often overlooks a more comprehensive evaluation of shared characteristics across different etiologies.
Dataset Limitations and the Need for Comprehensive Data
A significant challenge in corneal opacity research is the scarcity of publicly accessible datasets. The existing resources generally garner images from single imaging modalities, limiting their utility and generalizability across various clinical scenarios. Moreover, many datasets comprise small sample sizes and images focused on specific pathologies, making them inadequate for training robust AI models.
To address these gaps, recent efforts have resulted in the creation of a novel multimodal dataset that includes AS-OCT images from patients with various types of corneal opacity, along with corresponding ASPs. This dataset aims to encompass a broad spectrum of etiologies, such as trauma, infectious keratitis, and post-keratoplasty opacification. The meticulous annotation process involved collaborating with trained medical professionals, ensuring accuracy and reproducibility in the dataset.
Advancing Corneal Opacity Research
The introduction of this multimodal dataset is poised to significantly impact the standardization and quantification of corneal opacity-related research. By offering robust data, the hope is to foster AI-based tools that enhance clinical decision-making and improve personalized treatment workflows for patients suffering from corneal opacity.
Key Contributions of the Dataset
-
Diverse Image Acquisition: The dataset includes 2,992 AS-OCT images from cornea opacity cases, coupled with 187 corresponding ASPs, in addition to 3,280 AS-OCT images of normal corneas paired with 205 ASPs.
-
Expert Annotation: Image annotations were performed by three highly trained ophthalmologists, ensuring a high level of accuracy and reliability. Extensive hours were dedicated to this process, underscoring the commitment to creating a dependable resource for clinicians and researchers alike.
- Advanced Model Selection: For model development, established algorithms like UDTransnet, R34UNet, and MEGANET were chosen to represent both classical techniques and modern advancements in segmentation.
The hope is that, with access to this extensive dataset, medical professionals can more accurately identify and quantify corneal opacities, alleviating the reliance on manual annotation and accelerating the integration of deep learning technologies into clinical environments.
Conclusion
The landscape of corneal opacity assessment and treatment is on the brink of a transformation driven by technological advancements. The release of comprehensive and multimodal datasets, combined with the power of AI, might just hold the key to unlocking a future where patients receive more precise, effective, and individualized care for corneal opacity.