Evaluating Chatbot Performance in Tuberculosis-Related Medical Queries
In the rapidly advancing landscape of artificial intelligence, chatbots are emerging as vital tools in the realm of healthcare. Recent studies have evaluated the performance of three popular chatbots—ChatGPT, Copilot, and Gemini—using established criteria to assess their effectiveness in addressing medical inquiries, specifically related to tuberculosis. The results not only provide insights into their capabilities across various domains but also signal critical areas for enhancement in AI-assisted healthcare communication.
Performance Overview
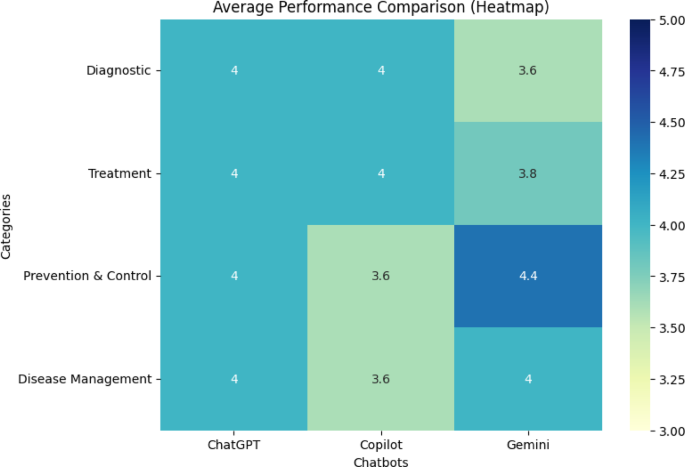
Table 1 outlines the mean scores achieved by each chatbot in four key categories: Diagnostic, Treatment, Prevention & Control, and Disease Management, based on the NLAT-AI criteria. Notably, in the Diagnostic category, all three chatbots scored an impressive 4.0, representing a remarkable uniformity in their diagnostic capabilities. This consistency underscores their potential utility as diagnostic assistants, providing reliable information to both health professionals and patients.
However, the nuances of chatbot performance become more apparent when examining the Treatment domain. Here, ChatGPT and Copilot both achieved a commendable score of 4.0, while Gemini lagged slightly with a score of 3.8. This disparity prompts questions about the specific indicators where Gemini may fall short, suggesting a necessity for focused refinements in its treatment-related algorithms.
Insights from the Prevention & Control Domain
Diving deeper into the Prevention & Control category, Copilot received the lowest score at 3.6. In contrast, Gemini excelled with a notable score of 4.4. This highlights Gemini’s robust capacity for addressing preventive measures and control strategies related to tuberculosis. Such performance can be crucial in public health initiatives, ensuring that users receive accurate information that might influence their health behaviors and choices.
Analyzing Disease Management Capabilities
When it comes to Disease Management, ChatGPT and Gemini both scored 4.0, demonstrating reliable performance. However, Copilot fell behind with a score of 3.6, revealing potential limitations in its ability to manage patient inquiries or suggest management strategies effectively. This divergence is significant, suggesting that users may benefit more from engaging with either ChatGPT or Gemini for comprehensive disease management advice.
Diagnostic Performance Evaluation
Table 2 sheds light on the diagnostic performance of the chatbots across specific indices. Here, Gemini, Copilot, and ChatGPT exhibited comparable performance with scores hovering around 4. This consistency in diagnostics echoes their capabilities evaluated previously. However, it is notable that the Gemini chatbot revealed weaknesses in the indices of Appropriateness and Effectiveness, where it scored a 3. This suggests an opportunity for improvement in how Gemini tailors its responses to be more suitable for user needs.
Treatment Domain Analysis
The scores in the Treatment domain, as depicted in Table 3, highlight that ChatGPT achieved a peak score of 5 in the Accuracy metric, outperforming both Copilot and Gemini. On the flip side, despite relatively lower scores in the Appropriateness metric, Copilot fared better than its counterparts. This indicates a complex interaction between accuracy and appropriateness—a vital consideration when selecting chatbot tools for healthcare information.
Performance in Prevention and Control
Table 4 distinctly points out that Gemini achieved top scores in the categories of Safety and Actionability, with perfect scores of 5 out of 5. These elements are crucial for any healthcare-related chatbot, indicating that Gemini is well-positioned to foster proactive health management practices among its users.
Insights from Disease Management Scores
In the Disease Management domain covered in Table 5, scores reflect a nuanced understanding of patient needs with all three chatbots achieving respectable scores of 4. However, it is concerning that Copilot’s performance in the Accuracy and Effectiveness indices trailed at 3 out of 5, suggesting gaps that could hinder its effectiveness in real-world applications.
Evaluating Chatbots on Brucellosis Queries
Table 6 presents an intriguing assessment using the DISCERN-AI criteria, examining how well each chatbot responds to inquiries about brucellosis. Here, ChatGPT shone in terms of Information Relevance, providing pertinent responses. However, Copilot and Gemini’s partial citation of sources brings an element of credibility. It’s essential in medical contexts for users to trust the information provided.
Despite differing strengths, all three chatbots displayed significant weaknesses, particularly in areas related to uncertainty indication and sourcing additional references. Recognizing these limitations is essential for continuing development in chatbot technology, particularly in a field as critical and sensitive as healthcare.
Closing Thoughts
As the evaluation of ChatGPT, Copilot, and Gemini reveal, while there is promising potential in AI chatbots for the distribution of healthcare information, ongoing developments are necessary to enhance performance, especially in aspects like providing thorough citations and addressing uncertainties. The current landscape reflects a stepping stone toward a future where AI can more effectively support healthcare professionals and patients alike in their information needs.