Artificial Intelligence: A Patent Perspective
Artificial intelligence (AI) is undeniably the buzzword of our time, transcending mere trend status to become a crucial indicator of technological evolution. For consumers, it foreshadows what innovations to expect from upcoming products. For patent attorneys, AI signifies the complexities of emerging technologies that will soon be pivotal in the patent landscape. Let’s explore the journey of AI-related patents over recent years.
The Rise of AI Patents
The publication of AI-related patents saw a noticeable surge starting in 2016, with 6,004 patents filed, ballooning to 11,334 in 2017. This trend has continued, with a staggering peak of 16,627 published last year alone, showcasing the robust growth in interest and investment in AI technologies.
Source: Patentscope search conducted for IPC code G06N; data retrieved on 28-05-2025.
The momentum in AI patent filings appears to show no signs of waning, signaling an ongoing commitment from various sectors to innovate and secure intellectual property in this burgeoning field.
Geographic Distribution of Patents
China holds the lion’s share of AI patent publications. The Chinese Patent Office (CNIPA) accounts for a staggering 64.3% of all AI-related patents filed globally, amounting to approximately 49,6811 patents. In stark contrast, the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) contributes about 16.9% of filings.
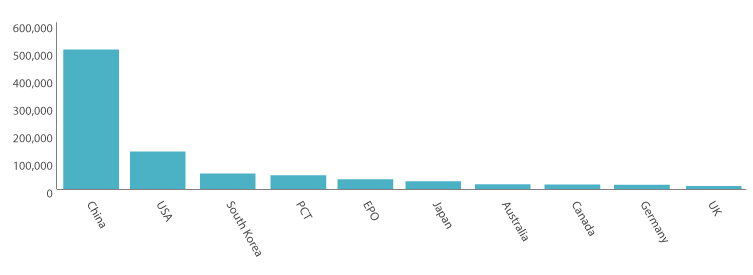
Source: Patentscope, based on the search conducted for IPC code G06N; data retrieved on 28-05-2025.
Other notable contributors include the Korean Intellectual Property Office, European Patent Office, and the German Patent and Trademark Office, with the latter three collectively accounting for a mere 4% of all publications.
Leading Innovators in AI Patents
The landscape of AI patent ownership is an intriguing mix of global powerhouses. Leading the charge is U.S.-based IBM, with an impressive 12,092 patents. Following closely is South Korea’s Samsung Electronics (8,118 patents) and U.S. tech giants Microsoft (5,968 patents) and Google (5,758 patents).
Top Patent Owners in AI Technologies
| Patent Owner | Number of Patents |
|---|---|
| International Business Machines Co | 12,092 |
| Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | 8,118 |
| Microsoft Tech Licensing LLC | 5,968 |
| Google LLC | 5,758 |
| Huawei Tech Co Ltd | 4,529 |
| Tsinghua University | 3,379 |
| Beijing Baidu Netcom Science and Tech Co Ltd | 4,092 |
| State Grid Co of China | 4,448 |
| Tencent Tech | 4,302 |
| Xiaomi Technology | 3,734 |
Source: Patentscope search conducted for IPC code G06N; data retrieved on 28-05-2025.
While Asia-based companies make a noteworthy appearance, U.S. firms retain a significant leadership role in patent filings among the global technological elite.
China’s Unique Approach
China’s staggering number of AI patents is tied to strategic governmental initiatives. The Chinese government has committed to fostering the tech sector through supportive regulations, funding, and policies that encourage innovation.
Support for Startups
The Chinese government’s push includes comprehensive guidelines aimed at bolstering financial services for technology firms. These initiatives strive to streamline capital flow, particularly for startups, by promoting investment in high-priority innovation areas.
The policies allow for flexible loan terms, insurance coverage enhancements, and foster venture capital collaboration. The five-year plan aims to significantly uplift tech innovation, encouraging lending that prioritizes technological advancements.
Driven by government policies and increased venture capital, China has cultivated a vibrant ecosystem of unicorns—privately held startups valued at over a billion dollars—second only to the United States. Cities like Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen are hubs for these companies, especially in the fields of AI, biotechnology, and semiconductors.
Regulatory Frameworks and Challenges
Angela Zhang’s book, High Wire: How China Regulates Big Tech and Governs Its Economy, argues that China employs a "dynamic pyramid model" which allows for swift adaptations in its technology regulations. This flexibility can be pivotal as the AI field evolves rapidly.
Despite its ambitious goals, China faces challenges, particularly from global uncertainties and geopolitical tensions, notably with the U.S. implementing export controls affecting key sectors like semiconductors. As a response, China is concentrating on domestic innovation to strengthen its technological foundations.
Implications for the Future
The burgeoning patent activity in AI signals a promising yet complex future. Whether these patents transition into market-ready innovations remains to be seen. For various stakeholders—ranging from investors to tech companies—it’s crucial to stay attuned to these developments. Understanding the nuances of China’s strategic priorities, along with its regulatory landscape, will be key to navigating this evolving ecosystem effectively.
By delving into the patent dynamics surrounding AI, we uncover not only technological trends but also insights into global market directions, offering a glimpse into what lies ahead in the realm of artificial intelligence innovation.

