Communication is the Foundation of Medicine: The Role of Generative AI Voice Agents
Effective communication is at the heart of medicine. From diagnosing conditions to shared decision-making, the exchange between patients and clinicians influences health outcomes significantly. Yet, the landscape of healthcare is evolving rapidly, with increasing pressure from time constraints, staffing shortages, and administrative burdens making meaningful interactions more challenging. In this context, generative AI voice agents are emerging as innovative tools that could redefine patient-clinician communication.
The Challenges of Modern Healthcare Communication
Today’s health systems are grappling with a myriad of challenges. Clinicians often find themselves stretched thin, juggling multiple patients and tasks within tight timeframes, risking the quality of patient communication in the process. As administrative tasks pile up, opportunities for personalized dialogue diminish. Traditional chatbots, primarily designed for simple, pre-set interactions, often fall short in handling the nuanced conversations that healthcare scenarios demand. They typically lack the flexibility to respond to unique patient queries, leading to frustrations for both patients and healthcare providers.
Enter Generative AI Voice Agents
Generative AI voice agents are sophisticated conversational systems fueled by large language models. Unlike their predecessors, these agents can comprehend and produce natural speech in real-time, enabling dynamic and context-sensitive interactions with patients. This capability means they can understand unique patient data from electronic health records and prior conversations, fostering richer conversations that reflect individual patients’ concerns and context.
These voice agents are designed to engage patients in a more human-like manner than traditional chatbots. They have the ability to ask clarifying questions, detect nuanced symptoms described by patients, and utilize a wide array of data points to guide their interactions. The result is a conversational experience that mimics human dialogue, allowing for unprecedented fluidity in discussions.
Enhancing Patient Engagement and Care
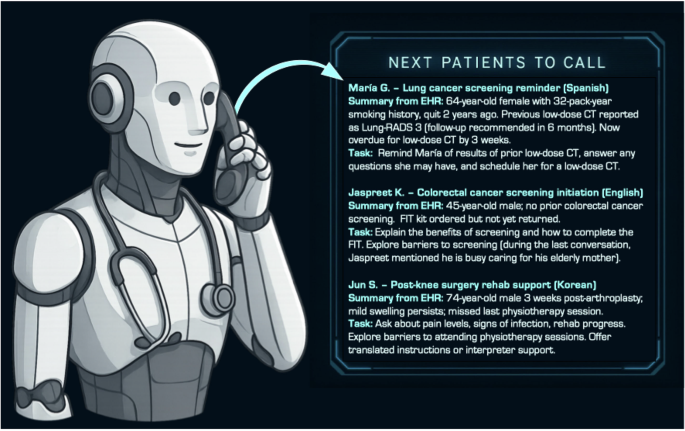
Generative AI voice agents can perform a variety of vital functions in healthcare. For instance, they can efficiently triage symptoms, conduct daily check-ins for chronic disease management, monitor medication adherence, and escalate concerns to human clinicians when necessary. This capability allows healthcare systems to identify early warning signs of crucial health changes—like shifts in a patient’s mood or symptoms—enabling timely interventions.
In a large-scale safety evaluation that reviewed over 307,000 simulated interactions, generative voice agents achieved accuracy rates in medical advice exceeding 99%. While this finding is preliminary and not peer-reviewed, it underscores the immense potential of these agents in supporting high-quality, patient-centered care.
Administrative Benefits
The advantages of generative AI voice agents extend beyond direct patient care; they also offer substantial operational benefits. These agents can handle administrative tasks such as billing inquiries, insurance verifications, appointment reminders, and rescheduling, thereby freeing up human resources for more complex responsibilities. They can also facilitate virtual appointments for patients facing mobility challenges, helping to minimize barriers to care.
Moreover, these AI agents can act as navigators for individuals with complex medical needs or limited health literacy. By enhancing pre-appointment education, they enable more meaningful interactions during clinical visits and better prepare patients for their healthcare encounters.
Transforming Population Health
One of the most exciting aspects of generative AI voice agents is their potential to improve population health outcomes on a scale that was previously unattainable. By enabling proactive, personalized outreach, health systems can increase engagement in preventive services, tailoring reminders for cancer screenings, vaccinations, or follow-up appointments according to individual patient profiles.
For instance, a recent study demonstrated that a multilingual generative AI voice agent improved colorectal cancer screening rates in underserved populations, achieving more than double the opt-in rate for a fecal immunochemical test among Spanish-speaking patients. When designed thoughtfully, these agents can bridge gaps in care and reduce disparities.
Overcoming Technical Hurdles
The road to widespread implementation of generative AI voice agents is not without its challenges. Key technical hurdles include latency issues, which can disrupt the flow of conversation, and accurate turn detection to discern patient responses. Enhancements in model performance, turn recognition, and cloud infrastructure are vital to optimizing the user experience and addressing these challenges.
Furthermore, safety remains a critical concern. Generative AI agents must recognize life-threatening scenarios to escalate them to human clinicians promptly. Building in robust clinical safety mechanisms will be essential for ensuring that patients receive the right guidance based on their specific health situations.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory environment for generative AI voice agents is also evolving. These tools may fall under the classification of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) when used for monitoring or diagnosing health conditions. As such, developers will need to navigate complex regulatory pathways to ensure safety and efficacy. Developing clear frameworks that categorize tasks by risk level—administrative, moderate-risk, and high-risk—can facilitate responsible deployment.
Ensuring User-Friendly Design
For generative AI voice agents to reach their full potential, user-centered design is paramount. Incorporating multiple communication modalities—like video calls or text messaging—can enhance accessibility and engagement among diverse patient populations. Devices must accommodate varying levels of digital literacy, including those with sensory impairments, to ensure inclusivity and usability.
Building Trust in AI
Public perception is crucial to the success of generative AI voice agents. Patients may initially approach these technologies with skepticism, influenced by negative experiences with robocalls or poorly designed chatbots. For sustained adoption, AI agents must be responsive, reliable, and demonstrate genuine empathy to build trust over time. Personalizing interactions by recalling past conversations and adapting language to cultural norms can help establish a sense of connectedness.
Workforce Integration and Training
The implementation of generative AI voice agents highlights the need for robust workforce integration. Clinicians, nurses, and administrative staff must undergo training to understand how to leverage these agents effectively, establishing clear pathways for escalation and intervention when necessary. Far from being a replacement for human labor, these AI tools can alleviate workloads, enabling healthcare providers to focus on complex cases.
Navigating Cost-Benefit Analyses
Finally, the adoption of generative AI voice agents requires a careful evaluation of costs and benefits. Organizations must weigh the financial investment against the potential for improved patient outcomes, operational efficiencies, and long-term savings. Questions about medication adherence rates, reduction in emergency visits, and administrative workload must inform the decision-making process to justify investments.
The integration of generative AI voice agents represents a transformative shift in the healthcare landscape, expanding the reach of personalized, responsive communication. While challenges remain, the thoughtful application of this technology promises to elevate patient care, improve health outcomes, and streamline administrative processes in an increasingly complex healthcare environment.