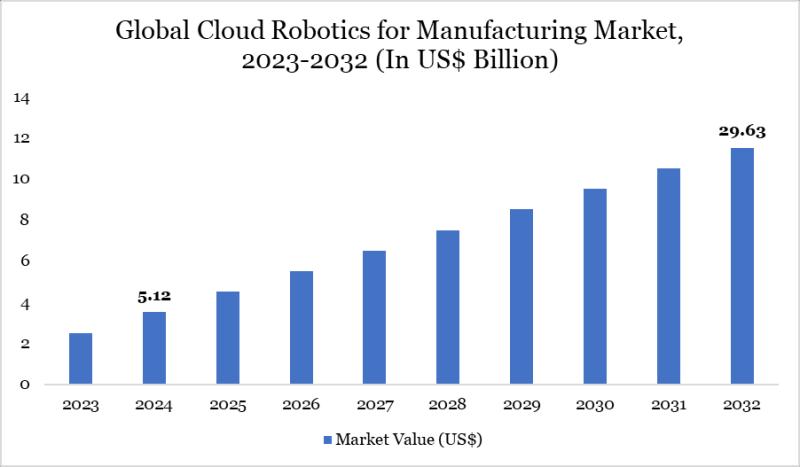
“U.S. Cloud Robotics in Manufacturing: Market Growth Ahead”
U.S. Cloud Robotics in Manufacturing: Market Growth Ahead
In an age where agility is paramount, the fusion of cloud computing and robotics is reshaping the manufacturing landscape. Imagine a factory where robots not only execute tasks but also adapt intelligently to shifts in production demands. This is not merely fantasy; it is a looming reality tightly tied to the rapid growth of cloud robotics. By leveraging cloud-based systems, U.S. manufacturers can streamline operations, improve collaboration, and enhance decision-making efficiency. Yet, if embraced hastily without due diligence, these innovations bear the potential for unforeseen complications, raising a crucial question: How can organizations balance the promise of cloud robotics with the practicalities of real-world implementation?
Understanding Cloud Robotics
Definition: Cloud robotics integrates cloud computing with robotic systems to enhance their capabilities and facilitate collaborative processes.
Example: Consider an automotive assembly line where robots equipped with sensors communicate data metrics to a cloud platform. This allows real-time adjustments based on analytics, boosting production efficiency.
Structural Deepener:
-
Comparison Model: Feature Traditional Robots Cloud Robotics Data Processing On-device Cloud-based Scalability Limited to hardware Near-limitless Intelligence Fixed algorithms Adaptive, real-time learning
Reflection: What underlying assumptions about manufacturing might lead professionals to overlook the integration of cloud technologies?
Practical Closure: Manufacturers must recognize that cloud robotics facilitates not just automation but also adaptive learning, enabling them to pivot swiftly in response to market needs.
The Importance of Data Security
Definition: Data security in cloud robotics refers to the protection of sensitive manufacturing data stored in cloud systems from breaches and cyber threats.
Example: A major electronics manufacturer recently suffered a cyberattack that compromised production schedules and confidential blueprints. Had they prioritized data security, the disruption might have been mitigated.
Structural Deepener:
- Lifecycle of Data Security in Cloud Robotics:
- Data Capture: Robots relay performance data to the cloud.
- Data Encryption: Data is encrypted during transit and at rest.
- Access Control: Stringent protocols determine who can access sensitive information.
- Incident Response: A well-established protocol ensures immediate action in case of breaches.
Reflection: What other vulnerabilities exist if the organization’s cyber defenses are insufficient against evolving threats?
Practical Closure: By investing in robust cybersecurity measures, manufacturers can safeguard their innovations and preserve trust with clients and partners.
The Role of Interoperability
Definition: Interoperability in cloud robotics ensures that various robotic systems and software platforms can communicate and work together efficiently.
Example: Imagine a logistics warehouse utilizing robots from multiple manufacturers. Achieving interoperability means that these robots can sync their operations, minimizing downtime and errors.
Structural Deepener:
- Taxonomy of Interoperability:
- Level 1: Basic Data Exchange
- Level 2: Functional Integration
- Level 3: Adaptive Collaboration
Reflection: What legacy systems could hinder the seamless integration of new cloud robotics solutions in a factory setting?
Practical Closure: Embracing open standards and protocols increases the likelihood of interoperability, leading to smoother operational rhythms and reduced friction.
The Impact on Workforce Dynamics
Definition: Workforce dynamics describe the shifting roles of human workers alongside increasing robotic automation.
Example: In factories adopting collaborative robots (cobots), humans are reassigned to more strategic roles, such as system oversight and quality control, rather than repetitive tasks.
Structural Deepener:
- Process Map of Workforce Transition:
- Task Identification: Determine tasks suitable for automation.
- Training Programs: Equip workers to oversee robotic operations.
- Feedback Loop: Continuous evaluation of worker-job match post-implementation.
Reflection: How might the transition to automated systems challenge existing labor relations and workplace morale?
Practical Closure: Engaging workforce training initiatives fosters adaptability and mitigates the anxiety surrounding job displacement.
Adapting to Market Changes
Definition: Adapting to market changes involves restructuring operations to align with shifting consumer demands and technological advancements.
Example: A manufacturer shifting from mass production to on-demand custom products demonstrates agility driven by cloud robotics.
Structural Deepener:
- Decision Matrix for Market Adaptation:
- Criterion 1: Customer Demand
- Criterion 2: Production Capacity
- Criterion 3: Technology Investment
Reflection: What assumptions about market predictability might stifle an organization’s agility?
Practical Closure: Manufacturers should embrace flexible production strategies enabled by cloud robotics, allowing for swift responses to consumer shifts.
Future Directions in Cloud Robotics
As we look ahead, the potential for cloud robotics in the U.S. manufacturing sector seems endless. The integration of AI and machine learning can provide even deeper data analytics, ensuring that robotic systems continuously learn and adapt. However, the road to cloud robotics is not linear. It requires a careful reassessment of existing processes, proactive strategies toward data security, and ongoing commitment to workforce development.
The dynamic interplay of technology and human capital in the realm of cloud robotics presents both a challenge and an opportunity for U.S. manufacturers in 2025 and beyond. Engaging with these complexities offers not just a glimpse into the future of manufacturing but practical tools for immediate action—a dual advantage that could well define success in an evolving industrial landscape.