“Enhancing Public Values in R&D with Natural Language Processing”
Enhancing Public Values in R&D with Natural Language Processing
Understanding Public Values in R&D
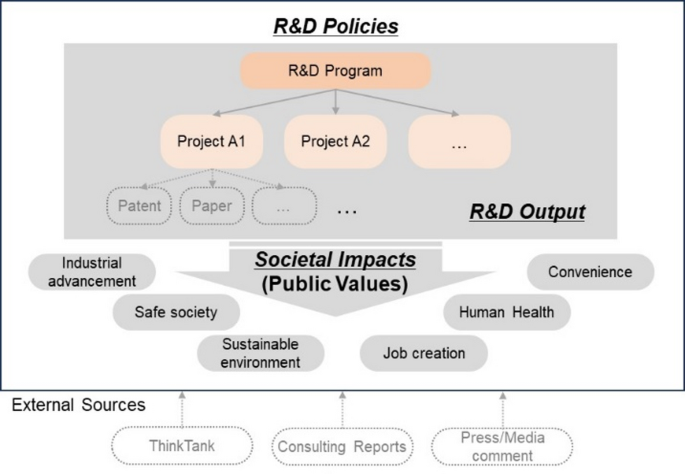
Public values refer to the societal benefits derived from research and development (R&D) activities. This encompasses a range of contributions, including advancements in technology, health improvements, and environmental protection. The significance of public values lies in their ability to shape the direction of R&D investments and initiatives, ensuring that taxpayer-funded research delivers tangible benefits to society.
For instance, consider AI advancements in healthcare. The development of AI-powered diagnostic tools not only speeds up diagnoses but can also lead to better health outcomes and cost savings for healthcare systems. This highlights how R&D can center on public values, making societal impact a focal point.
The Role of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence focused on the interaction between computers and human languages. It enables machines to read, understand, and derive meaning from text. In the context of R&D, NLP can evaluate and extract information from vast amounts of unstructured data, such as patents, research papers, and news articles, thereby illuminating different dimensions of public value.
For example, using NLP to analyze patent documents can reveal innovation trends and their implications for job creation or environmental benefits. This capability provides crucial insights for policymakers and researchers, making R&D activities more closely aligned with public interest.
Key Components of Public Value Evaluation
Evaluating public values in R&D necessitates several key components, including data collection, content analysis, and impact assessment. Each component offers unique insights and contributes to a comprehensive understanding of how R&D outputs translate to societal benefits.
-
Data Collection: Gathering relevant texts from patents, academic publications, and external sources like news articles is the foundation. For instance, extracting data from databases like the National Technology Information Service (NTIS) provides a database of public R&D outcomes, which is critical for subsequent analyses.
-
Content Analysis: By employing advanced NLP techniques, the textual data can be systematically analyzed to identify themes related to public values, such as “safe society” or “sustainable environment.” This might involve using models like GPT-3.5 to extract relevant phrases and classify information accordingly.
- Impact Assessment: Lastly, evaluating the societal impact involves linking the analytical outputs from the previous steps to broader public policy goals. This might include analyzing how specific R&D projects contribute to societal welfare or technological competitiveness.
By integrating these components, researchers can develop a framework that ensures R&D aligns closely with public needs and expectations.
Step-by-Step Lifecycle of Value Extraction
The lifecycle of public value extraction using NLP involves several chronological steps:
-
Data Acquisition: Begin by amassing documents related to R&D outputs. Utilize resources such as patent databases and academic journals to gather a rich dataset.
-
Preprocessing: Prepare the text data for analysis. This might involve cleaning the data to remove irrelevant information and standardizing formats.
-
Analytical Model Deployment: Leverage NLP models like GPT-3.5 for evaluating the content. This step transforms raw text into structured insights through classification and extraction of relevant public value themes.
- Evaluation and Reporting: Finally, assess the findings in relation to existing R&D policies. This involves synthesizing the extracted insights into actionable reports that inform future strategy.
The systematic execution of these steps ensures a robust evaluation of public values derived from R&D activities.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
A case worth examining is the development of AI algorithms for urban planning. Researchers utilized NLP to analyze various urban studies and policies to determine how AI solutions could improve public transportation efficiency. By extracting key themes related to “sustainable environment” and “convenience of life,” they demonstrated potential enhancements in urban living quality and infrastructure resilience.
Their findings influenced local governance R&D allocations, showcasing how NLP can translate technical knowledge into actionable public benefits. The integration of public value considerations in future urban planning ensured that societal needs were placed at the forefront of technological deployment.
Common Pitfalls in Public Value Assessment
When evaluating public values in R&D, pitfalls can arise that may skew findings or misrepresent impacts. One common issue is relying solely on quantitative metrics, which often overlook qualitative aspects of public value. For instance, while a project might show significant financial returns, it may fail to demonstrate its societal benefits, such as community well-being or environmental sustainability.
To avoid this, researchers must ensure a balanced approach that integrates both qualitative narratives and quantitative data. Engaging with diverse stakeholders for insights can further enrich the evaluation process, capturing a full spectrum of public value dimensions.
Tools and Frameworks for Evaluation
Several tools and frameworks exist to facilitate public value evaluations in R&D. The use of NLP models for text classification, such as BERT or RoBERTa, allows for nuanced insights into public value extraction. These models offer advantages in language understanding and can be tailored to specific contexts.
When selecting tools, factors such as dataset size and desired accuracy must be considered. For instance, GPT-3.5 is effective for large-scale analyses but may require fine-tuning for specialized tasks. Utilizing multiple models could also provide comprehensive insights and enhance reliability.
Variations and Alternatives in Public Value Frameworks
Different frameworks for public value assessment exist; their effectiveness can vary based on the specific R&D domain or stakeholder requirements. For example, theory-driven evaluation frameworks might focus on hypothesized pathways, while participatory approaches engage users throughout the evaluation process to gather wider insights.
The choice of methodology may depend on the nature of the R&D outputs and the specific societal impacts being assessed. It’s essential for researchers or policymakers to weigh these options carefully to ensure alignment with core public value principles while maximizing societal benefits.